- Also: Moskva, Mockba.
- Fyodor Michailovich Dostoyevsky (1821-1881) was born in Moscow.
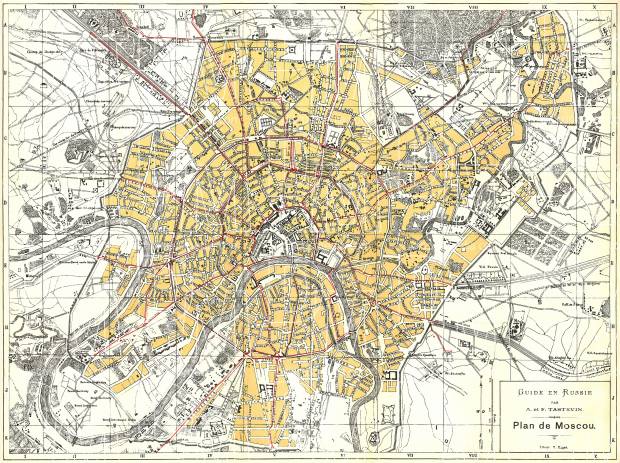
- Year 1897.
Moscow ceased to be Russia’s capital (except for a brief period from 1728 to 1732 under the influence of the Supreme Privy Council) when Peter the Great moved his government to the newly built City of St Petersburg on the Baltic coast in 1712.
Year 1897. Map City of Moscow.
After losing the status as capital of the empire, the population of Moscow at first decreased, from 200,000 in the 17th century to 130,000 in 1750. But after 1750, the population grew more than tenfold over the remaining duration of the Russian Empire, reaching 1.8 million by 1915. (1,038,625 in 1897).
Moscow is situated on the banks of the Moskva River, which flows for just over 500 km (311 mi) through the East European Plain in central Russia.

1898. Red Square. City of Moscow.
By 1700, the building of cobbled roads had begun. In November 1730, the permanent street light was introduced, and by 1867 many streets had a gaslight. In 1883, near the Prechistinskiye Gates, arc lamps were installed. In 1741 Moscow was surrounded by a barricade 25 miles (40 kilometres) long, the Kamer-Kollezhskiy barrier, with 16 gates at which customs tolls were collected.
Its line is traced today by a number of streets called val (“ramparts”). Between 1781–1804 the Mytischinskiy water-pipe (the first in Russia) was built. In 1813 a Commission for the Construction of the City of Moscow was established. It launched a great program of rebuilding, including a partial replanning of the city-center.
Among many buildings constructed or reconstructed at this time were the Grand Kremlin Palace and the Kremlin Armoury, the Moscow University, the Moscow Manege (Riding School), and the Bolshoi Theatre. In 1903 the Moskvoretskaya water-supply was completed.
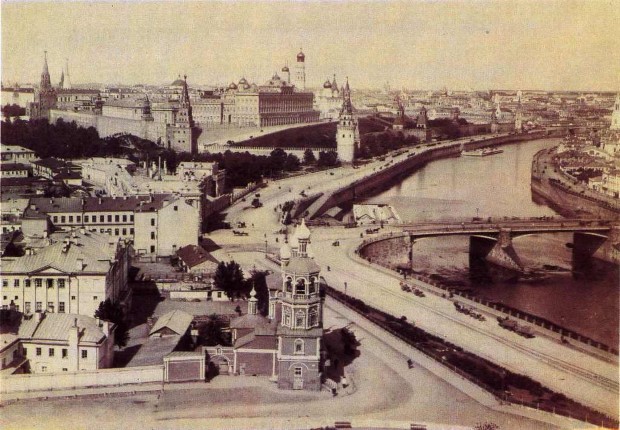

1900. City of Moscow.
In the early 19th century, the Arch of Konstantino-Elenensky gate was paved with bricks, but the Spassky Gate was the main front gate of the Kremlin and used for royal entrances. From this gate, wooden and (following the 17th-century improvements) stone bridges stretched across the moat.
Books were sold on this bridge and stone platforms were built nearby for guns – “raskats”. The Tsar Cannon was located on the platform of the Lobnoye mesto.
The road connecting Moscow with St Petersburg, now the M10 highway, was completed in 1746, its Moscow end following the old Tver road which had existed since the 16th century. It became known as Peterburskoye Schosse after it was paved in the 1780s.
Petrovsky Palace was built in 1776–1780 by Matvey Kazakov as a railway station specifically reserved for royal journeys from Saint Petersburg to Moscow, while coaches for lesser classes arrived and departed from Vsekhsvyatskoye station.

Red Square. City of Moscow.
When Napoleon invaded Russia in 1812, the Moscovites were evacuated. It is suspected that the Moscow fire was principally the effect of Russian sabotage. Napoleon’s Grande Armée was forced to retreat and was nearly annihilated by the devastating Russian winter and sporadic attacks by Russian military forces. As many as 400,000 of Napoleon’s soldiers died during this time.
Moscow State University was established in 1755. Its main building was reconstructed after the 1812 fire by Domenico Giliardi. The Moskovskiye Vedomosti newspaper appeared from 1756, originally in weekly intervals, and from 1859 as a daily newspaper.

1900. Verskaya Street. City of Moscow.
The Arbat Street had been in existence since at least the 15th century, but it was developed into a prestigious area during the 18th century. It was destroyed in the fire of 1812 and was rebuilt completely in the early 19th century.
In the 1830s, general Alexander Bashilov planned the first regular grid of city streets north from Petrovsky Palace. Khodynka field south of the highway was used for military training. Smolensky Rail station (forerunner of present-day Belorussky Rail Terminal) was inaugurated in 1870.
Sokolniki Park, in the 18th century the home of the tsar’s falconers well outside of Moscow, became contiguous with the expanding city in the later 19th century and was developed into a public municipal park in 1878. The suburban Savyolovsky Rail Terminal was built in 1902.
In January 1905, the institution of the City Governor, or Mayor, was officially introduced in Moscow, and Alexander Adrianov became Moscow’s first official mayor.

Moskva River. City of Moscow.
When Catherine II came to power in 1762, the city’s filth and smell of sewage was depicted by observers as a symptom of disorderly life styles of lower-class Russians recently arrived from the farms.
Elites called for improving sanitation, which became part of Catherine’s plans for increasing control over social life. National political and military successes from 1812 through 1855 calmed the critics and validated efforts to produce a more enlightened and stable society.
There was less talk about the smell and the poor conditions of public health. However, in the wake of Russia’s failures in the Crimean War in 1855–56, confidence in the ability of the state to maintain order in the slums eroded, and demands for improved public health put filth back on the agenda.