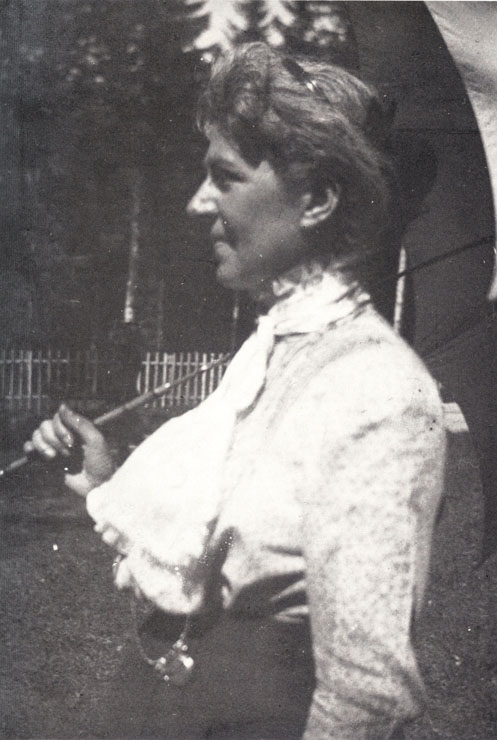
Year 1895. Natalie Bauer-Lechner (1858-1921).
During a composition competition, the young Gustav Mahler has a fight with the conductor of the student orchestra, who refuses to perform a symphony of his. This scene makes an indelible impression on Natalie. From the very beginning, she sympathized with the genius – as she says – that runs into a wall of unwillingness and incomprehension in this world. With her sensitive nature, Natalie has an eye for the difficult tasks of the artist, for which he is destined by his talent and destiny. She also has the psychological insight and the intellectual and literary capacities to put this on paper in an impressive way. From the beginning of the 1890s, a deep bond of friendship flourishes between them, which will continue until Mahler’s engagement with Alma at the end of 1901. Progressive, feminist, pacifist, autonomous.
During the 1890s she spent almost every summer with the Mahlers at their vacation address. Gustav Mahler always composed in the summer months. She witnessed the completion of Symphony No. 2, the creation of Symphonie No. 3 and no. 4 and the beginning of Symphony No. 5. She also witnessed the revision of Symphony No. 1 and the composition of Des Knaben Wunderhorn and Ruckert Lieder.
She has been present at dozens of performances of operas and symphonies under his leadership and has also witnessed the first performances of Mahler’s own works in the Austrian and German concert halls.
- Profession: Viola player, violinist.
- Residences: Vienna.
- Relation to Mahler: Love affairs (Year 1892 in Berchtesgaden and Year 1901 in one of the last nights of the summer holiday in Maiernigg in which Mahler rescues a drunken drowned person from the lake), member of Pernerstorfer Circle (member), biographer.
- Correspondence with Mahler:
- 03-11-1895 Letter to Natalie Bauer-Lechner (1858-1921). About Symphony No. 3.
- Born: 09-05-1858 Penzing, Vienna XIV. Natalia Anna Juliana Lechner.
- Father: Rudolf Lechner (1822-1895), bookseller and publisher in Vienna.
- Mother: Julie Lechner-Winiwarter (1831-1905).
- Sister: Ellen (Helene) Schlenk-Lechner (1859-1940). (Born 28-07-1859 Penzing, Died 24-03-1940 Vienna). Aged 80. Violinist. She founded a string quartet in 1909 and left a few compositions.
- Brother: Oskar Lechner (1868-1928). His wife: Antonie Lechner-Riessberger (1869-1956). His daughter: Gretl Donebauer (1897-1949).
- Sister: Minna Wilhelmine Drexler-Lechner (?-1934). Her husband: Prof. Friedrich Drexler (1858-1945). Her daughter: Friederike Killian-Drexler (1885-1952) who was married to Johann Killian (1879-1959). Son of Friederike (1885-1952) and Johann Killian (1879-1959) is Herbert Killian (1926-2017).
- Marriage: 27-12-1875. To widower and teacher at the university Dr. Alexander Bauer (1836-1921). Chemist. Natalie aged 17, Alexander aged 39. Unclear circumstances. Natalie had to play the role of foster mother for the three children from the earlier marriage of Alexander. It is claimed that the youngest child (Wilhelmine) was actually from Natalie, but this has not been proven.
- Divorce: 19-06-1885. After 10 years.
- Died: 08-06-1921 Vienna, Austria. Dies in poverty. Aged 63.
- Buried: 11-06-1921 Central cemetery, Vienna, Austria. Grave 59B-G1-21.
Chronology
- 1866-1872: Conservatory of Vienna with her sister Ellen. Graduated Violin and Viola. Aged 14.
- 1875: Early marriage. Aged 17.
- 21-06-1877: Presumably present at a composition competition at the Conservatory of Vienna, in which Gustav Mahler (1860-1911) participates. Gustav Mahler has a fight with the conductor of the student orchestra, Joseph Hellmesberger Sr. (1828-1893), who refuses to perform a symphony of his. It’s the first time she sees Gustav Mahler (1860-1911). 1877 Concert Vienna 21-06-1877 (piano).
- Year 1890: Meeting with Gustav Mahler in Budapest. In the fall. Start of their friendship.
- Year 1891: Meeting with Gustav Mahler in Bad Gastein.
- Year 1892: Meeting with Gustav Mahler in City of Berchtesgaden. Summer holiday.
- 1895: As a viola player, member of the Soldat-Roger String Quartet. Founder: Marie Soldat-Roeger (1863-1955) (Roeger, discovered by Johannes Brahms (1833-1897), pupil of Joseph Joachim (1831-1907)). ‘Damen-Streichquartett’ or ‘Ladies String Quartet’. International tours.
- 06-1896: Gustav Mahler lived a few days with Natalie Bauer-Lechner (1858-1921) in 1896-1896 House Natalie Bauer Vienna – Jasomirgottstrasse No. 3. Year 1896.
- 24-06-1897: Letter by Natalie Bauer-Lechner (1858-1921) to Rosa Papier-Paumgartner (1858-1932) about Mahlers relationship with Anna Bahr-von Mildenburg (1872-1947).
- 09-1901: Romantic meeting in one of the last nights of the summer holiday in Maiernigg.
- 01-1902: Permanently withdraws from the life of Gustav Mahler after his engagement with Alma Mahler (1879-1964). Withdrawal could have been also 09-1901.
- 1905: Letter to Johann Killian (1879-1959), publisher.
- 1907: Publication in Vienna of ‘Fragmente. Gelerntes und Gelebtes’ by Natalie Bauer-Lechner (1858-1921). About her life besides Gustav Mahler.
- 04-1912: Anonymous publication of excerpts from her diaries in Der Merker (Austrian magazine for music and theater).
- 1913: Ending of the Soldat-Roger String Quartet.
- 1917: Letter about Mahler’s love life to Hans Riehl (1891-1965) Austrian economist, sociologist and art historian. Love life Gustav Mahler. Published in 2014. 60 pages.
- 1918: In prison for publishing pacifist ideas. Caused serious health problems.
- 1920: Publication of extracts from her diaries in ‘Musikblatter des Anbruch’ under her own name.
- 1921: Died.
- 1923: Posthumous publication of ‘Erinnerungen an Gustav Mahler’ by Johann Kilian, the husband of her cousin Frederike.
- 1984: Publication of a more extensive edition of the ‘Erinnerungen an Gustav Mahler’ by Herbert Killian (1926-2017), the son of Johann Killian (1879-1959, Natalie’s second cousin). Author is Natalie Bauer-Lechner (1858-1921). Extension of the publication of 1923.
- 2010: Docudrama (video) ‘My Time Will Come’ – Gustav Mahler as remembered by Natalie Bauer-Lechner (2010). External link.
Natalie Bauer-Lechner (1858-1921) was an Austrian violist who is best known to musicology for having been a close and devoted friend of Gustav Mahler in the period between the end of her marriage in 1890 and the start of his to Alma Schindler in 1902. During this period, she kept a private journal which provides a unique view on Mahler’s personal, professional and creative life during and just after his thirties, including an exclusive preview of the structure, form, and content of his third symphony. See also Gustav Mahler Appearance.
She was the eldest child of five children (4 girls and 1 boy) born to the Viennese bookshop owner Rudolf Lechner (1822-1895) and his wife Julie, née von Winiwarter (1831-1905). She was educated privately, and later studied at the Vienna Conservatory.

Year 1897. Natalie Bauer-Lechner (1858-1921). Photo owned by Albrecht Spiegler, Vienna.

Year 1897. Natalie Bauer-Lechner (1858-1921).
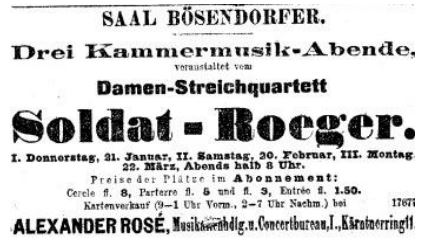
Year 1897. 21-01-1897. Soldat-Roger (Roeger) String Quartet. Natalie Bauer-Lechner (1858-1921).
At the conservatoire, she met Mahler for the first time: though she had graduated in 1872 and Mahler was a student from 1875-1878, she appears to have been able to use the Conservatoire’s facilities while her sister Ellen was still a student there. Bauer-Lechner became the violist of the all-female Soldat-Röger String Quartet, whose leader was the Joseph Joachim (1831-1907)-pupil Maria Soldat-Röger. As a trained professional musician, Bauer-Lechner grasped the technical and aesthetic content of Mahler’s conversation.
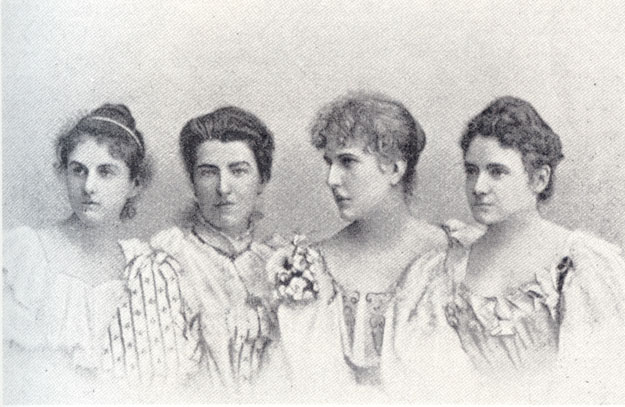
Year 1895. The original Soldat-Roger (Roeger) String Quartet: Ella Finger-Bailetti (1866-?), Natalie Bauer-Lechner (1858-1921), Lucy Müller-Campbell (1873-1944) and Marie Soldat-Roeger (1863-1955).
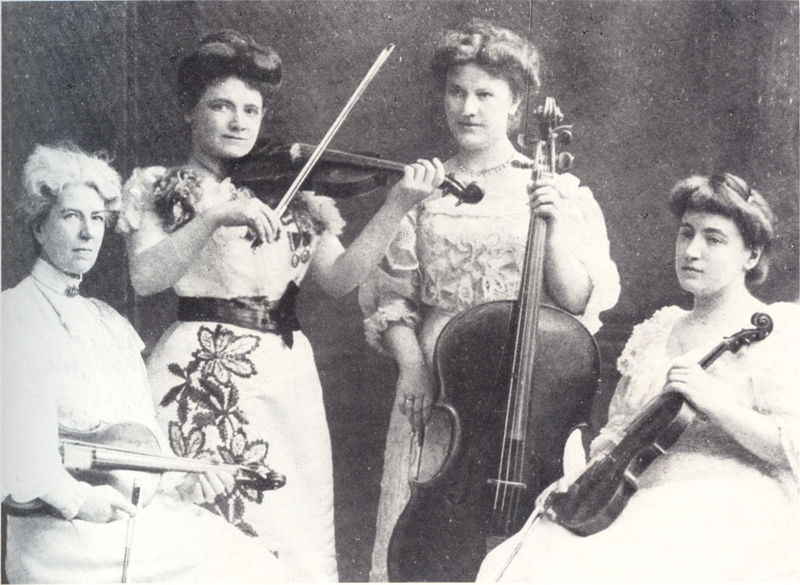

Soldat-Roger (Roeger) String Quartet (1895-1913): Natalie Bauer-Lechner (1858-1921), Marie Soldat-Roeger, Lucy Campbell and Ella Finger-Bailetti.
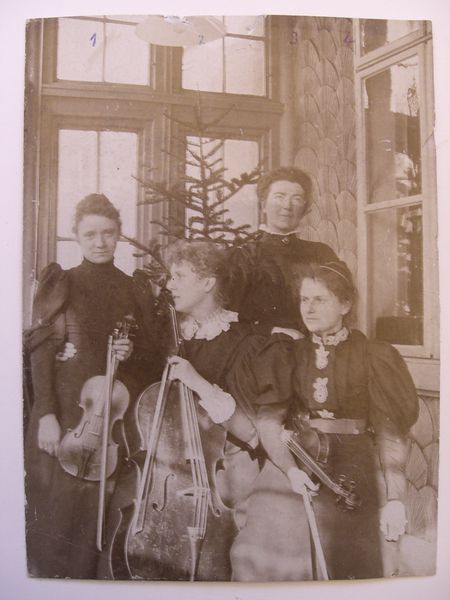

Natalie Bauer-Lechner (1858-1921) in Soldat-Roger (Roeger) String Quartet (1895-1913). Natalie Bauer in the back.
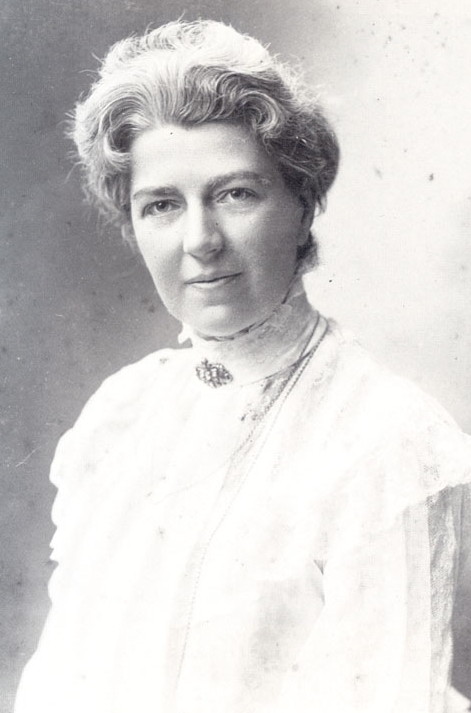

Year 1903. Natalie Bauer-Lechner (1858-1921).

30-03-1905. Year 1905. Letter Natalie Bauer-Lechner (1858-1921) to publisher Johann Killian (1879-1959) in Munich.

Year 1910 and Year 1911. Performances Natalie Bauer-Lechner (1858-1921).
She noted many of his statements about music, literature, philosophy and life at some length and apparently verbatim. In her later years, Bauer-Lechner became an outspoken feminist, and in 1918 published an article on the war and the need for female suffrage, which led to her arrest and imprisonment. Her health subsequently collapsed, and she died in poverty.
“Erinnerungen an Gustav Mahles” (“Recollections of Gustav Mahler”) 1890-1902 (published 1923)
1916. Natalie Bauer-Lechner (1858-1921). “Erinnerungen an Gustav Mahles” (“Recollections of Gustav Mahler”) 1890-1902 (published 1923). Médiathèque Musicale Mahler.
The publication history of her principal work is complicated. The source is a bulky collection of notes entitled Mahleriana, apparently deriving from some thirty diaries which no longer exist. During her life, brief extracts were published in two journals: anonymously in ‘Der Merker’ (April 1913), and under her own name in ‘Musikblätter des Anbruch’ (April 1920). Erinnerungen an Gustav Mahler was published in 1923, and represents an edited selection from the available materials (as does the later English volume Recollections of Gustav Mahler) (1980).
Currently owned by Mahler-scholar Henry-Louis de La Grange, the Mahleriana manuscript is not intact: numerous pages have been torn out by unknown hands, and there is no indication of what they might have contained. During her life, Natalie Bauer-Lechner was in the habit of lending her manuscript to friends and acquaintances (E.H. Gombrich reports that his parents had it in their possession for some time), and it is presumably this practice that allowed material to be removed.
A collection of notes recording conversations with Mahler’s long-standing friend Siegfried Lipiner (1856-1911) is understood to have once existed among her papers. Its current whereabouts are unknown. The director Beate Thalberg achieved a docudrama based on her diary: My time will come.
1916. Natalie Bauer-Lechner (1858-1921). “Erinnerungen an Gustav Mahles” (“Recollections of Gustav Mahler”) 1890-1902 (published 1923). Médiathèque Musicale Mahler.

1916. Natalie Bauer-Lechner (1858-1921). “Erinnerungen an Gustav Mahles” (“Recollections of Gustav Mahler”) 1890-1902 (published 1923). Médiathèque Musicale Mahler.
1916. Natalie Bauer-Lechner (1858-1921). “Erinnerungen an Gustav Mahles” (“Recollections of Gustav Mahler”) 1890-1902 (published 1923). Médiathèque Musicale Mahler.

1916. Natalie Bauer-Lechner (1858-1921). “Erinnerungen an Gustav Mahles” (“Recollections of Gustav Mahler”) 1890-1902 (published 1923). Médiathèque Musicale Mahler.
“Brief über Mahlers Lieben” (“Letter About Mahler’s Loves”) to Hans Riehl in 1917 (published 2011/2014)
Though musicologists who specialize in Gustav Mahler have long taken the memoirs of his wife, Alma, with a grain of salt, most of them have accepted her portrait of his as a fairly chaste ascetic who had few romances before he met her. Now, two scholars say a recently discovered letter from a Mahler confidante — and sometime lover — Natalie Bauer-Lechner, instead shows that he had numerous affairs and infatuations. “The letter is a fairly complete account of love affairs with quite a number of people, starting with his involvement with a woman named Josephine Poisl, the daughter of the postman in Iglau, his hometown,” said Stephen E. Hefling, one of the scholars, who hopes to publish the document.
The 59-page letter was handwritten in German and called “Brief über Mahlers Lieben” (“Letter About Mahler’s Loves”). “The letter is a fairly complete account of love affairs with quite a number of people, starting with his involvement with a woman named Josephine Poisl, the daughter of the postman in Iglau, his hometown,” said Stephen E. Hefling, one of the scholars, who hopes to publish the document.
The letter was written to Hans Riehl, one of Bauer-Lechner’s heirs, and should bring a new dimension to a composer whose titanic symphonies and bittersweet songs have become an increasingly central part of the classical repertory over the last 50 years, but who is often seen as an intensely brooding, introspective figure.
Now he may be seen as less severe, and at times fairly randy. (Bauer-Lechner does not discuss whether Mahler had any affairs after his marriage. That was Alma’s department: Mahler’s despair on discovering her romance with the architect Walter Gropius caused him to seek advice from Sigmund Freud.)

1917. Natalie Bauer-Lechner (1858-1921). “Brief über Mahlers Lieben” (“Letter About Mahler’s Loves”) to Hans Riehl in 1917 (published 2011). Médiathèque Musicale Mahler.
More
Bauer-Lechner, a violist, is hardly unknown in Mahler circles. The journal she kept during their long friendship (they met as students) was published in 1923, two years after her death (and 12 years after Mahler’s, at 50) and is regarded as an important way around what some Mahler specialists call “the Alma Problem,” meaning the nearly exclusive control of information about Mahler that his widow wielded for so many years. “Bauer-Lechner is one of the most important direct sources to Mahler, especially concerning the years before he married Alma,” said Steve Bruns, the associate dean for graduate studies for the College of Music at the University of Colorado, Boulder, and an organizer of the annual Colorado MahlerFest. “Her journals have been valuable to anyone who loves Mahler, not just specialists. I’ve only heard excerpts of the letter, but its wit and style really impressed me, as well as what a perceptive musical mind she had. That’s probably why Mahler took her seriously.”
Henry-Louis de La Grange, whose mammoth, multivolume “Gustav Mahler” is regarded as the definitive work on the composer — and who was one of the first to see the new letter — said that Bauer-Lechner is “of huge importance” and a trustworthy source. “In her journals, she is so honest about so many things, and we would lack a great deal if we didn’t have them,” Mr. de La Grange said by telephone from Toblach, Italy. Mr. Hefling, a director of the Gustav Mahler New Critical Edition and a professor of music at Case Western Reserve University, in Cleveland, and Morten Solvik, a Norwegian Mahler specialist, are editing a new version of Bauer-Lechner’s journal that will include passages that have never been published, as well as the new letter.
They have submitted an article that includes and analyzes the letter’s text to Musical Quarterly, a journal. Bauer-Lechner wrote the letter to Riehl (who, as far as Mahler scholars know, was a close friend, not a relative) in February 1917, apparently as a solution to what she regarded as a delicate problem: though she intended to publish her journals, she wrestled with the question of including Mahler’s confidences about his relationships with women. She regarded it as important information that posterity would value, but also considered it improper to include such details. Bauer-Lechner said in the letter that by writing it, she was leaving the problem in Riehl’s hands.
But Riehl did nothing to make the letter public, and it remained unknown to Mahler scholars until 2011, and even then, they nearly missed it. “It surfaced at an auction at the Dorotheum,” Mr. Hefling said in a telephone interview, referring to the Viennese auction house, “which is not a place that Mahler scholars or manuscript hunters look, because they deal mostly in jewelry and furniture. And it did not reach the minimum, which was not very high — something like 3,000 euros. If I’d known about it I would have found the money myself.”
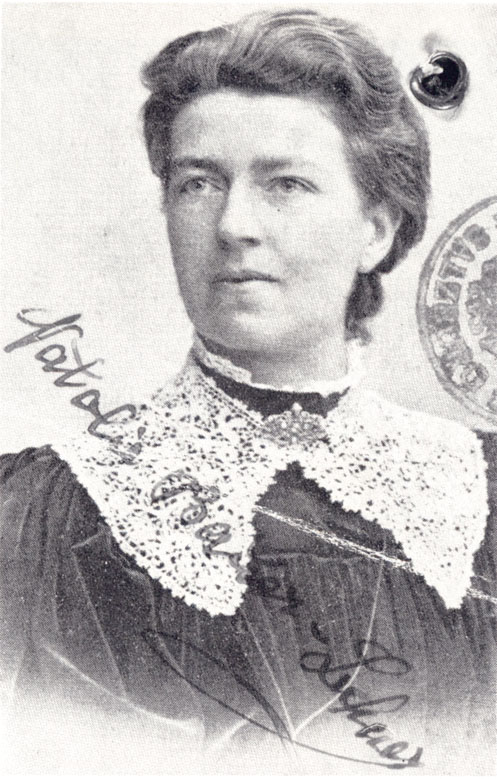
1919. 24-11-1919. Natalie Bauer-Lechner (1858-1921).
Mr. Hefling and Mr. Solvik were pointed to the letter by an assistant at the International Gustav Mahler Society in Vienna, and learned that it had found its way to a shop there that specializes in antiquarian items. But when they contacted the shop, they learned that the music librarian of the Austrian National Archives had beaten them to it. The original is in the archives, but Mr. Hefling and Mr. Solvik obtained a copy and set about translating it, and provided excerpts. Among the paramours discussed in the letter are Marion von Weber, who was married at the time to the grandson of the composer Carl Maria von Weber, and several opera singers, most notably the sopranos Rita Michalek, Selma Kurz and Anna von Mildenburg — who, Bauer-Lechner wrote, told her that their romance was platonic. See Love life Gustav Mahler.
Though his connections with several of the women mentioned in the letter have long been known, Bauer-Lechner’s recollections offer a more nuanced view of Mahler’s emotional makeup. Her discussion of Mahler’s affair with Ms. Marion von Weber-Schwabe (1856-1931), for example, reveals just how important it was. “It was very passionate, and Mahler seems to have been very naïve about it,” Mr. de La Grange said. “He and Marion told her husband themselves that they were in love, and they thought that he would be touched by the fact. But instead, he put a stop to it.”
Mr. Hefling added that the details of the romance put the chronology of the Symphony No. 2 into a new perspective. Mahler started the work in 1888, at the peak of his involvement with Ms. Weber, but set it aside after writing only one movement. He then essentially stopped composing until 1892, when he began settings songs from “Des Knaben Wunderhorn.” He returned to the symphony in 1893, and completed it the following year. After Ms. Weber’s husband insisted that she stop seeing Mahler, the composer moved from Leipzig to Prague to take his next position.

Natalie Bauer-Lechner (1858-1921).
He thought he had persuaded Ms. Weber to join him outside Munich, near Tutzing, but she didn’t show up. “This, according to Natalie, this is the main reason there is such a long gap in the chronology of the Second Symphony,” Mr. Hefling said. “What Natalie tells us is that he was very depressed, and his creativity wasn’t there. And she more or less credits herself with reigniting it by giving him confidence. She believed in his genius.” Bauer-Lechner wrote about her own affair with Mahler as well, in fairly purple prose. “As we were immured in the very narrow room and isolated from all the world in fervently animated Scheherazade-like tales, up until the graying of morning, we unfolded our entire lives before each other,” she wrote. “Without declaration, question, and vow, our psyches and physiques melted into each other.”
The letter also offers new detail about Mahler’s relationship with his siblings, particularly his sister Justine (Ernestine) Rose-Mahler (1868-1938) — who, it turns out was the rock on which most of Mahler’s early romances (include the one with Bauer-Lechner) foundered. As the eldest surviving son, Mahler looked after his siblings after their parents died, in 1889, and for a while, Justine moved in with him. “The reason all these affairs broke off, according to Natalie,” Mr. Hefling said, “was Justine’s extreme jealousy and possessiveness.” Bauer-Lechner may have inadvertently been the reason Alma was able to break through that obstacle, Mr. Hefling said.
Justine helped break them up but this time, Bauer-Lechner wrote, “she buried herself beneath the ruins of the temple while it crashed down upon us.” “For not only did she bring about the severance of our lives forever,” she wrote, “she also robbed herself of his whom she would not grant to anyone else. “Reading between the lines,” Mr. Hefling said, “at that point, Mahler told Justine that this couldn’t continue.” It was only a matter of weeks before he became smitten with Alma.
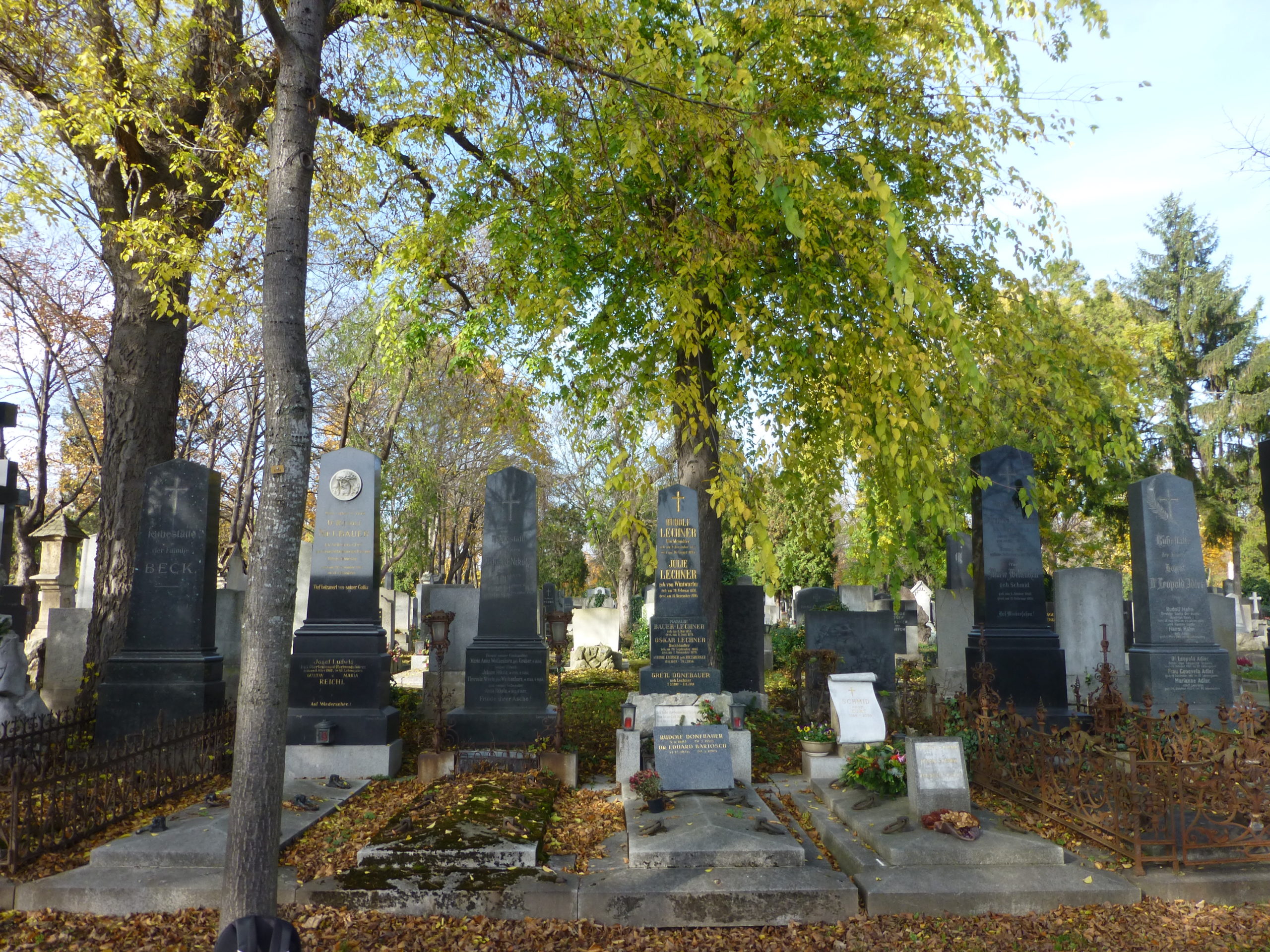

Grave Natalie Bauer-Lechner (1858-1921). Central cemetery, Vienna.

Grave Natalie Bauer-Lechner (1858-1921). Central cemetery, Vienna.



